Emotional Intelligence
Reason Leads To Conclusions, Emotion Leads To Action
Emotions Get In The Way Or Get You On The Way
What Is Emotional Intelligence?
The concept of "Emotional Intelligence" also referred to as "Emotional Quotient" [EQ] rose to prominence as a behavioural model with Daniel Goleman's 1995 book of the same name.
The original theory was developed twenty years previously by psychologists Howard Gardner , Peter Salovey and John 'Jack' Mayer.
The EQ model suggests that the conventional measure of intelligence [IQ], is too narrow and that there are wider areas of the emotional dimension that have a significant bearing on how we behave and perform in social and work situations, and thus on our success.
Goleman defines emotional intelligence as:
"The capacity for recognizing our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships"
He proposes that this is a learned capability. In other words, unlike the traditional measures of intellectual intelligence which cannot be learned, we can learn, practise and develop competencies that will expand and increase our emotional intelligence.
The 2 key themes
- Understanding yourself, your goals, intentions, responses, behaviour and all
- Understanding others, and their feelings
Goleman identified five key competencies of EQ as:
- Knowing your emotions.
- Managing your own emotions.
- Motivating yourself.
- Recognising and understanding other people's emotions.
- Managing relationships, i.e. managing the emotions of others.
Emotional Intelligence - Overview by Daniel Goleman
Emotional Intelligence - The 5 Competencies
Personal Skills
This is about how we manage ourselves, for example: optimism, persistence in pursuing goals despite obstacles and setbacks
- Self-awareness - Knowing one’s internal states, preferences, resources and intuitions
# Emotional awareness - Recognizing one’s emotions and their effects
# Accurate self-assessment - Knowing one’s strengths and limits
# Self-confidence - A strong sense of one’s self-worth and capabilities - Self-regulation - Managing one’s internal impulses and resources
# Self-Control - Keeping disruptive emotions and impulses in check
# Trustworthiness - Maintaining standards of honesty and integrity
# Conscientiousness - Taking the responsibility for personal performance
# Adaptability - Flexibility in handling change
# Innovation - Being comfortable with novel ideas, approaches, and new information - Motivation - Emotional tendencies that guide or facilitate
reaching goals
# Achievement drive - Striving to improve or meet a standard of excellence
# Commitment - Aligning with goals of the group or organization
# Initiative - Readiness to act on opportunities
Social skills
This is about how how we manage relationships, for example:team capabilities, creating group synergy in pursuing collective goals
- Empathy - Awareness of other’s feelings, needs, and concerns
# Understanding others Sensing others’ feelings and perspectives, and taking active interest in
their concerns
# Developing others - Sensing others’ development needs and bolstering their abilities
# Service orientation - Anticipating, recognizing, and meeting customers’ needs
# Leveraging diversity - Cultivating opportunities through different kinds of people
# Political awareness - Reading a group’s emotional currents and power relationships - Social Skills - Adeptness and inducing desirable responses in
others
# Influence - Wielding effective tactics for persuasion
# Communication - Listening openly and sending convincing messages
# Conflict management - Negotiating and resolving disagreements
# Leadership - Inspiring and guiding individuals and groups
# Change catalyst - Initiating or managing change
# Building bonds - Nurturing instrumental relationships
# Collaboration & cooperation - Working with others toward shared goals
How To Use Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence can be applied in many different areas of your life, and it will include some of the following behaviours:
- Accepting criticism and responsibility
- Not dwelling on mistakes and failures and moving on
- Saying No when it is appropriate and you need to
- Appropriately displaying empathy and sharing your feelings
- Building win-win solutions that benefit all parties
- Listening mindfully
- Self knowledge about your own motives and drivers
- Non judgemental in your assessments of others' behaviours
The 7 Habits Of Emotionally Intelligent People
Resources
Emotional Intelligence - Review [slide presentation]
Emotional Intelligence - Assessments
Emotional Intelligence - Book Review
Return to: Managing Personal Change
- What if everything we think…
LATEST ARTICLES
The Power Of Patience - Why You Need The World's Toughest Quality
 Nothing in the world can take the place of patience. Patience and persistence are omnipotent. In everyday life, patience is often overshadowed by the desire for immediate results. We live in an era of…
Nothing in the world can take the place of patience. Patience and persistence are omnipotent. In everyday life, patience is often overshadowed by the desire for immediate results. We live in an era of…Demonizing The Other and Personal Acts Of Compassion
 What Does Demonizing The Other Mean? Demonizing the other refers to the act of portraying a group of people or an individual as inherently evil, threatening, or inferior. It often serves to justify di…
What Does Demonizing The Other Mean? Demonizing the other refers to the act of portraying a group of people or an individual as inherently evil, threatening, or inferior. It often serves to justify di…Why You Should Embrace Anomalies - The Incredible Value Of Disconfirming Evidence
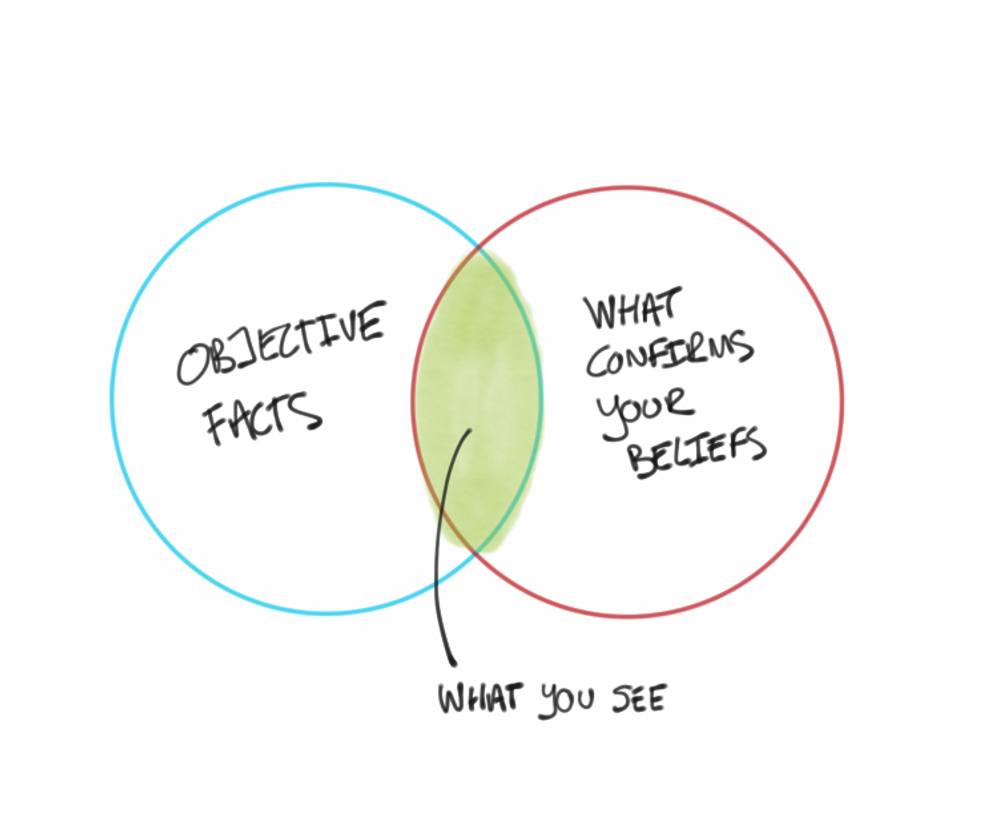 Is Your Desire To Be Right Greater Than Your Desire To Have Been Right? An anomaly is a deviation from what is expected or commonly regarded as the norm. It often appears as an unexpected observation…
Is Your Desire To Be Right Greater Than Your Desire To Have Been Right? An anomaly is a deviation from what is expected or commonly regarded as the norm. It often appears as an unexpected observation…Amazing Grace - The Majesty And The Mercy of Freedom From Your Pain
 "I once was lost, but now I am found, was blind, but now I see." The hymn and popular song "Amazing Grace" was written 250 years ago by John Newton, a former slave trader who in 1748 nearly died in a…
"I once was lost, but now I am found, was blind, but now I see." The hymn and popular song "Amazing Grace" was written 250 years ago by John Newton, a former slave trader who in 1748 nearly died in a…The Transformative Power Of Acceptance
 Experience The Power Of Acceptance. This website contains about 500,000 words. You could read every single word and it wouldn't make any real difference to you. You might become better informed, but t…
Experience The Power Of Acceptance. This website contains about 500,000 words. You could read every single word and it wouldn't make any real difference to you. You might become better informed, but t…Inversion - The Power Of Opposite Thinking
 How To Avoid The Unwanted Outcome. The power of opposite thinking, also known as inversion, lies in its ability to stimulate creativity, enhance problem-solving, and provide a fresh perspective on cha…
How To Avoid The Unwanted Outcome. The power of opposite thinking, also known as inversion, lies in its ability to stimulate creativity, enhance problem-solving, and provide a fresh perspective on cha…Are You Aligned With Reality? Or Do You See What You Believe?
 We tend to see that which aligns with what we believe, and to act upon that rather than acting on reality. Being aligned with reality starts with a clear and accurate understanding of the world. It me…
We tend to see that which aligns with what we believe, and to act upon that rather than acting on reality. Being aligned with reality starts with a clear and accurate understanding of the world. It me…The Law Of Response and Outcome
 A New Approach To A New Life At time of writing we are entering a new year which is traditionally a time of making resolutions to change our behaviour and improve the quality of our lives. And yet pow…
A New Approach To A New Life At time of writing we are entering a new year which is traditionally a time of making resolutions to change our behaviour and improve the quality of our lives. And yet pow…Clear Thinking - Turning Ordinary Moments Into Extraordinary Results
 There are two ways to handle the world - try to predict, or try to prepare. "Clear Thinking" by Shane Parrish, published in Oct 2023, is a laudable testament to the art of cogent thinking, and will be…
There are two ways to handle the world - try to predict, or try to prepare. "Clear Thinking" by Shane Parrish, published in Oct 2023, is a laudable testament to the art of cogent thinking, and will be…Self Dialogue - Working With Your Many Selves
 Self Dialogue Is About Working With ALL Levels Of Your Mind. The key to effective self dialogue is to have tools, techniques and resources that work with all levels of your mind. This simple self-faci…
Self Dialogue Is About Working With ALL Levels Of Your Mind. The key to effective self dialogue is to have tools, techniques and resources that work with all levels of your mind. This simple self-faci…The Balanced Brain - The Ultimate Route To Personal Transformation
 How To Experience The Benefits Of A Balanced Brain. Underpinning all of the belief systems and practices that offer routes to personal change, transformation and spiritual growth is the balanced brain…
How To Experience The Benefits Of A Balanced Brain. Underpinning all of the belief systems and practices that offer routes to personal change, transformation and spiritual growth is the balanced brain…How To Make Better Decisions - By Avoiding The Narrative Trap
 To Understand The Truth We Have To See The Whole Picture. One of the best ways to make better decisions is to have a deeper understanding of the many things that might stop that happening. To understa…
To Understand The Truth We Have To See The Whole Picture. One of the best ways to make better decisions is to have a deeper understanding of the many things that might stop that happening. To understa…The Greatest Love - The Most Important Relationship You Will Ever Have
 Yet Most Will Never Know It Everyone of us has a place, in our hearts there's a space, that is home to the greatest love of all. This love transcends everything we think we know about the world of for…
Yet Most Will Never Know It Everyone of us has a place, in our hearts there's a space, that is home to the greatest love of all. This love transcends everything we think we know about the world of for…Everything Is Connected And Why You Don't Feel It
 ...And Why It Matters
As human beings we are skating on very thin ice with our sense of self and certainty about "how things are" and what we like to think of as reality:
...And Why It Matters
As human beings we are skating on very thin ice with our sense of self and certainty about "how things are" and what we like to think of as reality:
Who Is In Charge Of Your Brain?
 How Not To Be Stupid. Who is in charge of your brain? This is not a silly questions. It matters because the outcomes that you experience in your life are determined by how you respond to the events th…
How Not To Be Stupid. Who is in charge of your brain? This is not a silly questions. It matters because the outcomes that you experience in your life are determined by how you respond to the events th…How To Be A Winner On A Very Large Scale
 The Incredible Benefits Of Selective Attention. This is not a typical article about how to be a winner. We are not going to talk about goal setting, the importance of habits, the power of focus and al…
The Incredible Benefits Of Selective Attention. This is not a typical article about how to be a winner. We are not going to talk about goal setting, the importance of habits, the power of focus and al…The Metagame Approach To Life
 How To Achieve Your Biggest Objectives.
The metagame approach to life is all about winning and achieving your biggest objectives by:
- Understanding the bigger picture
How To Achieve Your Biggest Objectives.
The metagame approach to life is all about winning and achieving your biggest objectives by:
- Understanding the bigger picture
- Being better by doing things d…Shantideva - The Way Of The Bodhisattva
 Walking The Path Of Compassion. Shantideva the 8th century Indian Buddhist sage is famous for his treatise "The Way of the Bodhisattva" delivered as an extended teaching to the monks of Nalanda monast…
Walking The Path Of Compassion. Shantideva the 8th century Indian Buddhist sage is famous for his treatise "The Way of the Bodhisattva" delivered as an extended teaching to the monks of Nalanda monast…Reframing History - Deconstruction And Discussion Not Destruction
 History is always about context, not imposing our own moral values on the past. For those of us fortunate enough to live within western democracies, we are living in an age where a vociferous and into…
History is always about context, not imposing our own moral values on the past. For those of us fortunate enough to live within western democracies, we are living in an age where a vociferous and into…Tao Te Ching - Connecting To Your True Source Of Power.
 How To Be Lived By The Tao. The Tao Te Ching is one of those books that many people read, few understand, and even fewer put into practice. The only way to know the Tao is to experience it, and it is…
How To Be Lived By The Tao. The Tao Te Ching is one of those books that many people read, few understand, and even fewer put into practice. The only way to know the Tao is to experience it, and it is…How Things Really Are - The Inbuilt Design Flaws
 Chaos, Disorder And Decay Is The Natural Order Of Things. Nobody has the perfect life. We all struggle and strive to attain health, wealth and personal happiness. Yet these three big areas: our health…
Chaos, Disorder And Decay Is The Natural Order Of Things. Nobody has the perfect life. We all struggle and strive to attain health, wealth and personal happiness. Yet these three big areas: our health…Intuition Or Anxiety - Are There Angels Or Devils Crawling Here?
 How To Tell The Difference Between Intuition and Anxiety. How do you know whether the voice of your intuition is real or just the product of your inner anxiety? Several months ago I was having a drink…
How To Tell The Difference Between Intuition and Anxiety. How do you know whether the voice of your intuition is real or just the product of your inner anxiety? Several months ago I was having a drink…What Is Truth - How To Tell A Partial Truth From The Whole Truth?
 How the truth and nothing but the truth is often not the whole truth. My great aunty Flo broke her arm and died. It is true that she broke her arm in 1923. It is also true that she died in 1949. But t…
How the truth and nothing but the truth is often not the whole truth. My great aunty Flo broke her arm and died. It is true that she broke her arm in 1923. It is also true that she died in 1949. But t…Duality And Life Beyond Your Thinking Mind
 Duality and life beyond your thinking mind focuses on the limitations of time, foreground and background, duality and "stuckness". The first aspect of duality and life beyond your thinking mind focuse…
Duality and life beyond your thinking mind focuses on the limitations of time, foreground and background, duality and "stuckness". The first aspect of duality and life beyond your thinking mind focuse…The Conscious Mind Is Limited - Be Aware And Be Prepared
 Being aware is the first stage of being prepared. The conscious mind is limited in so many ways. There are some who would argue that there is no such thing as conscious thought and that it is represen…
Being aware is the first stage of being prepared. The conscious mind is limited in so many ways. There are some who would argue that there is no such thing as conscious thought and that it is represen…Your Inner Map Of Reality - Here's Why You Think The Way You Do
 The big picture of how your inner map of reality creates your feelings, thoughts, and behaviours. Your inner map of reality is based on the filters of your own ethnic, national, social, family and rel…
The big picture of how your inner map of reality creates your feelings, thoughts, and behaviours. Your inner map of reality is based on the filters of your own ethnic, national, social, family and rel…The Failure Of Cancel Culture - Suppression Not Engagement
 Why we need to wear our beliefs lightly and develop negative capability. Throughout history people have campaigned to fight beliefs, ideologies, and injustices that they perceived to be oppressive, di…
Why we need to wear our beliefs lightly and develop negative capability. Throughout history people have campaigned to fight beliefs, ideologies, and injustices that they perceived to be oppressive, di…4 Big Reasons Why We Get Stuck In Our Attempts At Personal Change
 Most People Spend Their Entire Life Imprisoned Within The Confines Of Their Own Thoughts. This first of the 4 big reasons why we get stuck is, in my view, the most important. The "self-help industry…
Most People Spend Their Entire Life Imprisoned Within The Confines Of Their Own Thoughts. This first of the 4 big reasons why we get stuck is, in my view, the most important. The "self-help industry…How Do I Change And Why Is It So Hard?
 We Would Rather Die Than Change, And We Usually Do In my experience, the vast majority of people who say they want to change don’t change. Most people reading this won’t change because they don’t real…
We Would Rather Die Than Change, And We Usually Do In my experience, the vast majority of people who say they want to change don’t change. Most people reading this won’t change because they don’t real…The Illusion Of A Separate Self - Windows 11 With Self Awareness!
 Beyond the content of your mind you are so much more than you think you are. When we talk of "myself" this is the conventional way of referring to our self image which is in fact the ego's constructio…
Beyond the content of your mind you are so much more than you think you are. When we talk of "myself" this is the conventional way of referring to our self image which is in fact the ego's constructio…
