|
Managerial GridKnowing When to Adopt A People Or Production Orientation
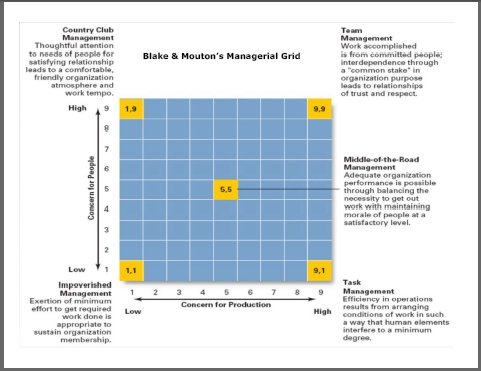
The Managerial Grid model (1964) is a behavioural leadership model developed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton. The model identifies four different leadership styles based around a focus of people and a focus on production. This can be thought of as a spectrum with task-orientation and affiliation orientation at either ends of that spectrum. The visual representation of their model uses two axes: (1) Concern for people is plotted along the vertical axis (2) Concern for task is along the horizontal axis They both are scaled on a range of 0 to 9
Finding The Most Appropriate Leadership Style
Most people fall somewhere near the middle of the two axes, but there are 4 polarised positions:
[1] Authoritarian[9 on task, 1 on people] Productivity is the absolute imperative! This management style is autocratic, rules based and sees punishment [or threats of punishment] as an effective way of motivating team members. Whilst this approach may deliver impressive production results at first, low team morale will eventually undermine. High performers will not tolerate this management style for long.
[2] Team Leader[9 on task, 9 on people] High on production/High on people. According to the Blake Mouton model, team management is the most effective leadership style. It reflects a leader who is equally passionate about his work as he is for the people he works with. Team managers prioritize both the organization's production needs and their people's needs. They do this by making sure that their team members understand the business objective purpose and they involve the team in determining production needs. When people are have a sense of ownership of the organisation's success, their needs and production needs coincide.
[3] Country Club[1 on task, 9 on people] High People/Low Results. The Country Club or "accommodating" style of manager primary concern is the team's needs and feelings. This is an affiliative management style that incorrectly assumes that, as long as the team are happy they will be productive.
Under this style the working environment is so laid back that productivity suffers as a result of a lack of control and direction.
[4] Impoverished[1 on task, 1 on people] The Impoverished or "indifferent" manager is largely ineffective. With a limited to non-existent focus on getting the job done, and with even less interest in motivating the team his results are disorganisation and dissatisfaction. Clearly the best place for a leader to be along the two axes at most times would be a 9 on task and a 9 on people i.e. the Team Leader. However, certain situations might call for one of the other three to be used at times. For example, by playing the Impoverished Leader, you allow your team to gain self-reliance; or by acting as an Authoritarian Leader to instill a sense of discipline in an unmotivated worker. According to the managerial grid model , by careful understanding of the requirements of the situation and the full context, you will know what style is the most appropriate and effective for the circumstances.
Return to: Define leadership Further Reading: Situational Leadership - Right person, right place, right time Home Page
|